Many people think of GitHub as a niche website that hosts open-source projects. In June 2018, that niche website with a mere 28 million users got more media attention than Apple’s Worldwide Developer Conference (WWDC). Somehow, a site that provides free services was so valuable that Microsoft acquired them for $7.5 billion US dollars.
Since its launch in 2007, GitHub has grown far beyond its roots as a web-based service that provides a hosted version of the Git-distributed version control system. The site hosts open-source projects and also offers paid plans for developers and companies. With the adoption of agile development and DevOps practices, it has become an essential part of the continuous integration/delivery/deployment pipeline for many companies. Not only do these companies host their source code in private GitHub repositories, but they also integrate their repositories with their continuous integration (CI) systems.
An important part of any CI system is the ability to run automated tests on any code committed to a source control repository. The automated tests help prevent new code from breaking the software built by the CI system. Now, with the release of the Applitools Eyes GitHub integration, you can include automated tests that perform visual UI testing as part of your build process. Visual UI testing lets you create tests that accurately simulate real users interacting with your software. The integration also takes care of uploading test results to Applitools’ advanced Automated Visual Management (AVM) system for analysis.
This post explains how you can use the Applitools Eyes GitHub integration to perform visual validations for pull requests. Integrating Applitools Eyes with GitHub prevents visual defects from merging into your production software. For each pull request, it merges the baseline screenshots of the branch along with your source code, and runs automated visual validation tests.
Applitools Eyes GitHub Integration
Applitools Eyes ensures your application looks and functions exactly as expected across all browsers, operating systems, devices, and screen resolutions. In addition to handling application testing, the Applitools Eyes GitHub integration lets you use Applitools Eyes as an integral part of your build automation process.
The Applitools Eyes GitHub integration automatically configures the baselines used for obtaining and saving test baselines. It displays the status of your tests directly in the pull request page, right next to the merge status. The integration lets you view the history of an application’s user interface (UI) and see how it has changed, what has been changed, and by whom. This will show you how your product’s UI has evolved over the product’s lifetime. The feature allows you to merge visual testing baseline branches in the same way you merge changes to your test and source code. For each branch in your GitHub project repository, you can see the history of all your test baselines, compare them to prior baseline versions, and if necessary, revert to an earlier version. This feature lets you reject and/or revert to any baseline you modified by accident or by design.
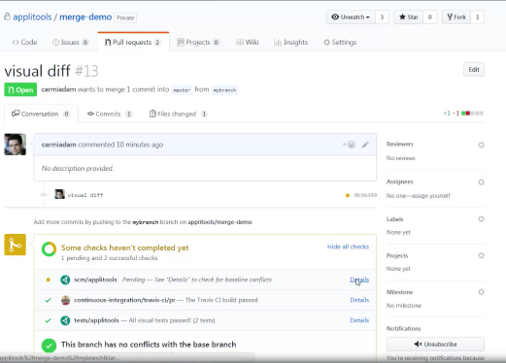
Visually Validating a Pull Request
In order to illustrate how to use the Applitools Eyes GitHub integration, we created a complete demo that includes all the relevant source code files and project-related assets. The demo is called merge-demo, and we made it available as a GitHub repository. The demo runs visual validation against the Applitools Hello World test page. The test navigates to the Hello World page, visually validates it, clicks the Click Me button, and visually validates the page. In this demo, the Hello World test code has been modified to test the page in two different viewport sizes.
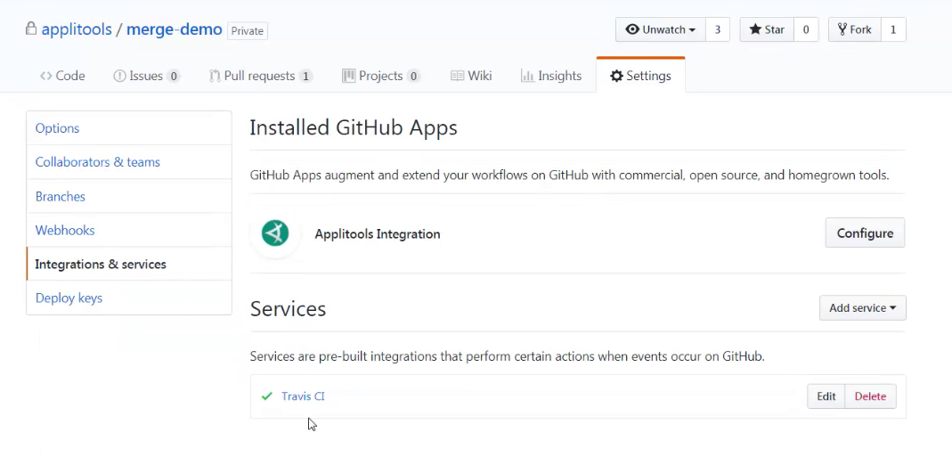
Configuring the Integration
Before you can run the demo, you need to install and configure the Applitools Integration application. In the merge-demo repo, open the Settings > Integration & Services page. The page indicates that the Applitools Integration application has been installed. The page also indicates that the Travis CI service has been configured to build and run tests.
Creating the Pull Request
To create the pull request on your PC, open a terminal window and clone the merge-demo locally. Create a new branch, called mybranch, and modify the tests. Commit the changes and push them back to the remote branch. Now, create a pull request to merge the changes with the master branch.
Building the Request
After receiving the Pull Request, Travis CI initiates a build for the pushed pull request. For the sake of simplicity, we recommend you disable the Builds for the Pushed Branches option; otherwise, Travis CI will build two individual branches.
When the build is complete, open the Pull Request page. The Test Applitools status indicates the status of all visual tests that ran as part of the build. We can see the two tests detected differences. If you click the details link, it will take you to the corresponding page in the Applitools Test Manager. The batch contains two tests with different viewport sizes. The test name includes the branch name, the name of the pull request, the source branch, the commit message, and the SHA. Using the page, you can accept the changes made to the first test and reject the changes made to the second test.
Managing and Merging Baselines
Reopen the Pull Request page and you will see the Status Description now indicates that one of the visual tests has been failed. If you accept the changes in the second test, you can see the status changes to green to indicate that all of the visual tests were passed. By looking in the Test Details, you can see the tests were configured to run in the source branch. After reviewing the test results, you save them to the baselines of the source branch. The updated baselines will not affect any tests running in other branches.
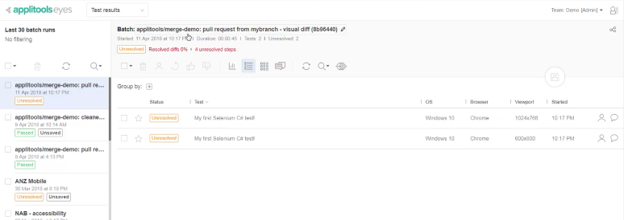
After updating your baselines, you can check that other team members did not make conflicting changes to the baseline. You can do this by checking the SCM status of the Applitools request, which is currently pending. Next, open the Pull Request page. This page displays the details of all the changes in the baselines, compares them, and allows you to edit the source baseline by porting ignore regions and locations from the target baseline, or by adding new ones. The page shows that the Applitools SCM status changed to green and no baseline conflicts were found. This means the two changes in the source branch are ready to be merged with the target branch. As soon as your source code is fully merged, Applitools will automatically merge the changed baseline in the source branch with the baseline of the target branch.
Visual UI Version Control
In a very short time, GitHub has grown from an obscure developer-centric website into an essential tool for a wide range of enterprises. It serves the needs of freelance contractors, large corporations, and governments. GitHub may have started as a cloud-based version control system, but today, it provides additional services such as project management, online documentation, web hosting, and defect tracking. For many companies, GitHub has replaced their on-premises source control management systems, and it functions as an essential piece of their CD/CI tooling.
In this post, we looked at how to use GitHub as part of your DevOps stack. We explained how the Applitools Eyes GitHub integration automatically configures the baselines used for obtaining and saving test baselines, how to create pull requests, and how you can add visual test validation to your CI pipeline.
This solution gives you powerful tools that ensure each time a pull request triggers a build and merges your target and source branches, it also gives you control and insight into the process. The integration also simplifies the process of reviewing and managing visual test baselines. More importantly, it is a form of UI version control that shows how your application’s UI has changed and evolved over time. These Applitools Eyes GitHub integration benefits will ensure the quality of your products and will benefit your end users and customers.
To read more about Applitools’ visual UI testing and Application Visual Management (AVM) solutions, check out the resources section on the Applitools website. To get started with Applitools, request a demo, or sign up for a free Applitools account.




